- 转载需注明出处
目录
- 1. 查看当前系统所使用的文件统的类型及版本号
- 2.阅读Ext3(或Ext4)文件系统,特别是索引节点相关的源代码
- 3.添加一个打印磁盘块号的系统调用
- 4.编写用户测试程序,测试filesys系统调用
1. 查看当前系统所使用的文件统的类型及版本号
root@binism-GE60-2OC-2OD-2OE:/home/binism# parted

p
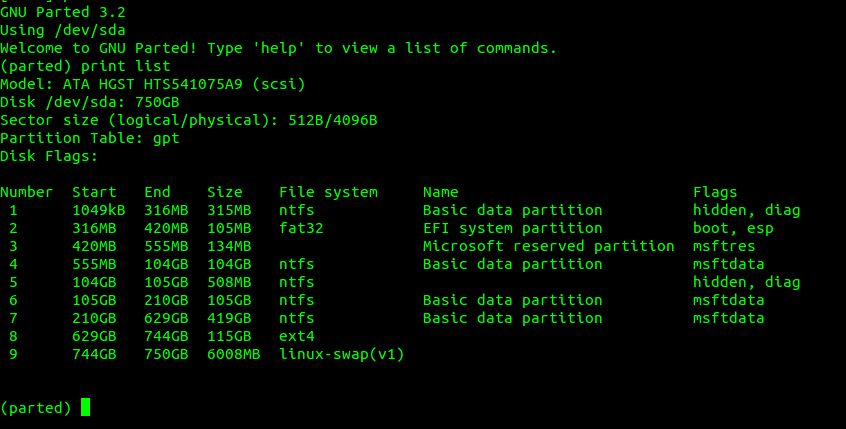
可以看到
- 我的电脑硬一共有9个分区,它们分别是NTFS、EXT4、格式的。
- linux系统所占的分区为第八分区,起始位置分别是629GB处和744GB处。总大小为115GB。文件系统版本为EXT4。
2.阅读Ext3(或Ext4)文件系统,特别是索引节点相关的源代码
这里对struct inode 和 struct file 进行注释:
- 索引节点对象由inode结构体表示,定义文件在linux/fs.h中
struct inode {
struct hlist_node i_hash; // 哈希表
struct list_head i_list; // 索引节点链表
struct list_head i_dentry; // 目录项链表
unsigned long i_ino; // 节点号
atomic_t i_count; // 引用记数
umode_t i_mode; // 访问权限控制
unsigned int i_nlink; // 硬链接数
uid_t i_uid; // 使用者id
gid_t i_gid; // 使用者id组
kdev_t i_rdev; // 实设备标识符
loff_t i_size; // 以字节为单位的文件大小
struct timespec i_atime; // 最后访问时间
struct timespec i_mtime; // 最后修改(modify)时间
struct timespec i_ctime; // 最后改变(change)时间
unsigned int i_blkbits; // 以位为单位的块大小
unsigned long i_blksize; // 以字节为单位的块大小。
在4.2.6中移出了这个变量
用 1<<i_blkbit代替
unsigned long i_version; // 版本号
unsigned long i_blocks; // 文件的块数
unsigned short i_bytes; // 使用的字节数
spinlock_t i_lock; // 自旋锁
struct rw_semaphore i_alloc_sem; // 索引节点信号量
struct inode_operations *i_op; // 索引节点操作表
struct file_operations *i_fop; // 默认的索引节点操作
struct super_block *i_sb; // 相关的超级块
struct file_lock *i_flock; // 文件锁链表
struct address_space *i_mapping; // 相关的地址映射
struct address_space i_data; // 设备地址映射
struct dquot *i_dquot[MAXQUOTAS]; // 节点的磁盘限额
struct list_head i_devices; // 块设备链表
struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe; // 管道信息
struct block_device *i_bdev; // 块设备驱动
unsigned long i_dnotify_mask; // 目录通知掩码
struct dnotify_struct *i_dnotify; // 目录通知
unsigned long i_state; // 状态标志
unsigned long dirtied_when; // 首次修改时间
unsigned int i_flags; // 文件系统标志
unsigned char i_sock; // 套接字
atomic_t i_writecount; // 写者记数
void *i_security; // 安全模块
__u32 i_generation; // 索引节点版本号
union {
void *generic_ip; // 文件特殊信息
} u;
};- struct file结构体定义在include/linux/fs.h中定义
struct file {
union {
struct list_head fu_list; //文件对象链表指针linux/include/linux/list.h
struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead; //RCU(Read-Copy Update)是Linux 2.6内核中新的锁机制
} f_u;
struct path f_path; //包含dentry和mnt两个成员,用于确定文件路径
#define f_dentry f_path.dentry // f_path的成员之一,当前文件的dentry结构
#define f_vfsmnt f_path.mnt // 表示当前文件所在文件系统的挂载根目录
const struct file_operations *f_op; //与该文件相关联的操作函数
atomic_t f_count; //文件的引用计数(有多少进程打开该文件)
unsigned int f_flags; // 对应于open时指定的flag
mode_t f_mode; //读写模式:open的mod_t mode参数
off_t f_pos; //该文件在当前进程中的文件偏移量
struct fown_struct f_owner; //该结构的作用是通过信号进行I/O时间通知的数据。
unsigned int f_uid, f_gid; //文件所有者id,所有者组id
struct file_ra_state f_ra; //在linux/include/linux/fs.h中定义,文件预读相关
unsigned long f_version;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *f_security;
#endif
// needed for tty driver, and maybe others
void *private_data;
#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
// Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file
struct list_head f_ep_links;
spinlock_t f_ep_lock;
#endif // #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
struct address_space *f_mapping;
};- 结构
struct dentry是目录项
struct dentry {
atomic_t d_count; //目录项对象使用计数器,可以有未使用态,使用态和负状态
unsigned int d_flags; //目录项标志
struct inode * d_inode; //与文件名关联的索引节点
struct dentry * d_parent; //父目录的目录项对象
struct list_head d_hash; //散列表表项的指针
struct list_head d_lru; //未使用链表的指针
struct list_head d_child; //父目录中目录项对象的链表的指针
struct list_head d_subdirs; //对目录而言,表示子目录目录项对象的链表
struct list_head d_alias; //相关索引节点(别名)的链表
int d_mounted; //对于安装点而言,表示被安装文件系统根项
struct qstr d_name; //文件名
unsigned long d_time; // used by d_revalidate
struct dentry_operations *d_op; //目录项方法
struct super_block * d_sb; //文件的超级块对象
vunsigned long d_vfs_flags;
void * d_fsdata; //与文件系统相关的数据
unsigned char d_iname [DNAME_INLINE_LEN];// 存放短文件名
}3.添加一个打印磁盘块号的系统调用
- 要求:为内核添加一个新的系统调用filesys, 其从调用者接收一个磁盘文件的全局路径名,打印该文件占用的所有磁盘块;
这个例子是我在stackoverflows上发现的,它实现了在用户空间对文件磁盘块号的打印。代码如下:
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int fd,
i,
block,
blocksize,
bcount;
struct stat st;
assert(argv[1] != NULL);
assert(fd=open(argv[1], O_RDONLY));
assert(ioctl(fd, FIGETBSZ, &blocksize) == 0);
assert(!fstat(fd, &st));
bcount = (st.st_size + blocksize - 1) / blocksize;
printf("File: %s Size: %d Blocks: %d Blocksize: %d\n",
argv[1], st.st_size, bcount, blocksize);
for(i=0;i < bcount;i++) {
block=i;
if (ioctl(fd, FIBMAP, &block)) {
printf("FIBMAP ioctl failed - errno: %s\n",
strerror(errno));
}
printf("%3d %10d\n", i, block);
}
close(fd);
}这段代码使用了函数ioctl(),这个函数并未在内核环境下定义,它相关实现在Linux/fs/ioctl.c中:
static int file_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg)
{
struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);
int __user *p = (int __user *)arg;
switch (cmd) {
case FIBMAP:
return ioctl_fibmap(filp, p);
case FIONREAD:
return put_user(i_size_read(inode) - filp->f_pos, p);
case FS_IOC_RESVSP:
case FS_IOC_RESVSP64:
return ioctl_preallocate(filp, p);
}
return vfs_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
}可以看见获取磁盘号的函数为ioctl_fibmap(),此函数同样定义在Linux/fs/ioctl.c中:
static int ioctl_fibmap(struct file *filp, int __user *p)
{
struct address_space *mapping = filp->f_mapping;
int res, block;
// do we support this mess?
if (!mapping->a_ops->bmap)
return -EINVAL;
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_RAWIO))
return -EPERM;
res = get_user(block, p);
if (res)
return res;
res = mapping->a_ops->bmap(mapping, block);
return put_user(res, p);
}此函数使用的几个宏定义,如EINVAL 、CAP_SYS_RAWIO 、EPERM等,
和使用的函数,如capable()、get_user()等, 在内核linux/include下的头文件中均有定义。
我们可以在系统调用的c文件中实现此函数,便可达到获取磁盘号的目的。
- 编写filesys.c文件
vim linux4.2.6/kernel/filesys.c
filesys.c
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/hdreg.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/unistd.h>
#include <linux/capability.h>
#include <uapi/linux/fs.h>
#include <uapi/asm-generic/ioctl.h>
#include <uapi/asm-generic/errno-base.h>
#include <uapi/linux/capability.h>
static int ioctl_fibmap(struct file *filp, int *p) {
struct address_space *mapping = filp->f_mapping;
int res, block;
// do we support this mess?
if (!mapping->a_ops->bmap)
return -EINVAL;
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_RAWIO))
return -EPERM;
block = *p;
res = mapping->a_ops->bmap(mapping, block);//获取第block有效磁盘块的磁盘块号
*p = res;
return 0;
}
static int file_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,unsigned int *arg){
//struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);
//int __user *p = (int __user *)arg;
switch (cmd) {
case FIBMAP:
return ioctl_fibmap(filp, arg);
}
return 0;
}
asmlinkage long sys_filesys(const char __user *argv){
printk(KERN_EMERG "filesys is running!\n");
struct file *fp;
struct inode *node;
fp = filp_open(argv, O_RDONLY, 0);
if(IS_ERR(fp)){
printk(KERN_EMERG "Open file %s error!\n", argv);
return -1;
}
node = fp->f_path.dentry->d_inode;
off_t F_SIZE = node->i_size;
unsigned int i,
filesize,
blocksize,
bcount;
filesize = (int)F_SIZE; //以字节为单位的文件大小;
bcount = node->i_blocks; //文件块数,这里的文件块数指的是inode上所有的磁盘块数包含无效的块;
blocksize = (1 << node->i_blkbits); //以字节为单位的块大小;
unsigned int block;
unsigned int bcount2 = (filesize + blocksize - 1) / blocksize;//这里是真正有效的磁盘块数;
printk("File: %s Size: %d Blocks: %u Blocksize: %d\n", argv, filesize, bcount2, blocksize);
for(i = 0; i < bcount2; i++){
block = i;
unsigned int *p = █
int tmp = ioctl_fibmap(fp, p);
if(tmp){ //映射失败;
printk(KERN_EMERG "FIBMAP ioctl failed - errno");
}
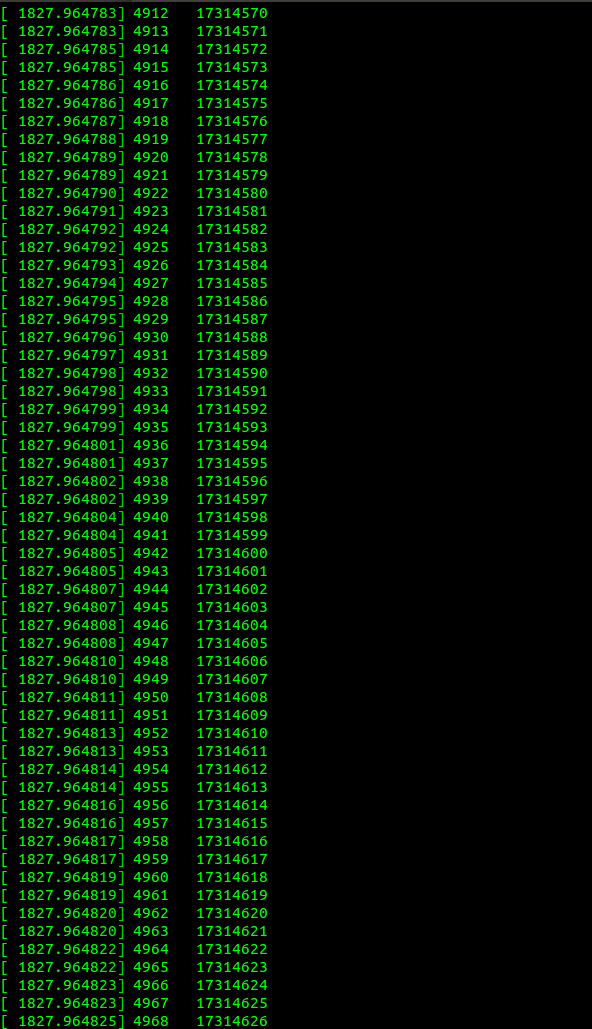
printk(KERN_EMERG "%3d %10d\n", i, block);//打印第i号磁盘块块号block;
}
filp_close(fp,NULL);
return 0;
}- 添加系统调用filesys
- 修改system table
cd ../linux-4.2.6/arch/x86/entry/syscalls
vim syscall_64.tbl

- 修改系统头文件
cd ../linux-4.2.6/include/linux
vim syscalls.h
在include/linux/syscalls.h文件的最后,#endif之前加入系统调用服务例程filesys;

- 编辑kernel目录下的Makefile文件
linux-4.6.2/kernel/Makefile
#
# Makefile for the linux kernel.
#
obj-y = fork.o exec_domain.o panic.o \
cpu.o exit.o softirq.o resource.o \
sysctl.o sysctl_binary.o capability.o ptrace.o user.o \
signal.o sys.o kmod.o workqueue.o pid.o task_work.o \
extable.o params.o \
kthread.o sys_ni.o nsproxy.o \
notifier.o ksysfs.o cred.o reboot.o \
async.o range.o smpboot.o \
+ filesys.o
- 编译安装内核
make -j 4
make modules_install
make install
4.编写用户测试程序,测试filesys系统调用
- 查看/boot目录下linux3.19.0的映像文件所占磁盘块
test.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#define __NR_mycall 323
int main(){
int ret = 0;
ret = syscall(__NR_mycall, "/boot/initrd.img-3.19.0-39-generic");
printf("return of hellosys is: %d\n", ret);
return -1;
}- 编译生成并运行
gcc -o test test.c
../test
- 查看结果
注:prink不会向控制台输出信息,查看printk输出内容可使用dmesg命令查看
dmesg | tail -5083
BINISM
/
/ - views
Published under(CC) BY-NC-SA 3.0 CN.